How to Know if You Have High Arch Feet
It is important to know your arch type in society to place and buy shoes that volition best support your bodyweight to salvage pes pain and preclude injuries such equally plantar fasciitis.
WHAT Dissimilar TYPES OF FOOT ARCHES ARE THERE?
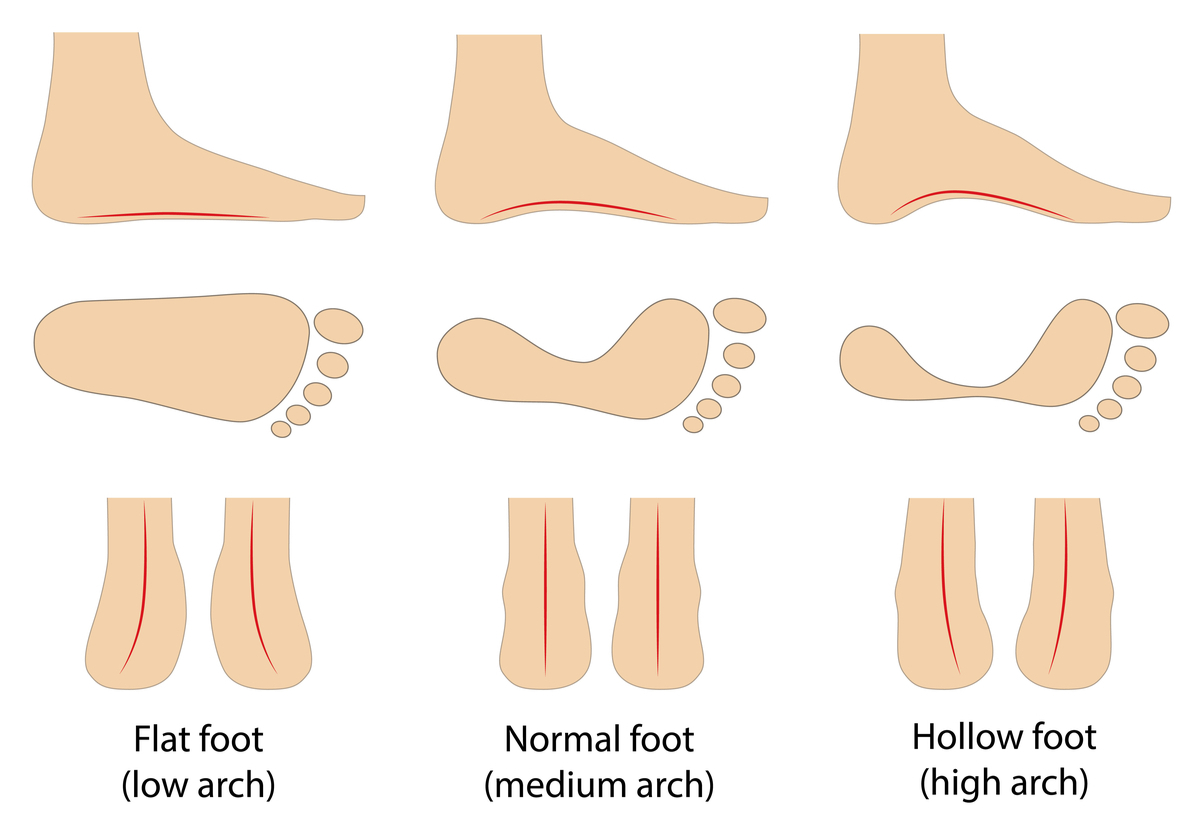
Flat feet: Pronation is a term used to describe the inward leaning motion of the pes and ankle bones towards the arch. The amount of pronation correlates with arch meridian. The more a person pronates, the flatter the arch will be.
Normal arch: The normal arch has the middle office of the curvation slightly raised from the ground when weight bearing. A expert examination is to try and skid a slice of newspaper below the arch. If you tin can identify the paper in between your pes and the flooring yous accept a normal arch.
High arch: High arches are a genetically inherited status where your arch is much higher or raised than normal. When weight bearing at that place is significantly more space in between the flooring and the curvation.
HOW TO DETERMINE YOUR Arch Blazon?
The easiest manner to determine your curvation blazon is to do a "dwelling house water test". Simply pour h2o into a shallow pan. Insert your foot into the pan to moisture the soles of your feet. Step onto a piece of paper and wait down.
Flat (Depression) curvation: If you see the arch more often than not filled in then your pes is nigh probable collapsing inwards when you run.
Normal arch: If you meet nearly half of your arch region then you accept the most common foot type. A normal arch supports your bodyweight and pronates normal.
High arch: If your arch has footling to no curvation than you have a high arch. Your foot is non arresting much shock when you run.
HOW DOES EACH Touch on YOUR GAIT?
Apartment feet: The amount of pronation correlates with curvation acme. The more a person pronates, the flatter the arch will be. Many people who over-pronate do not experience any hurting or discomfort. When flat feet become symptomatic, a thorough pes evaluation is recommended. Posterior Tibial Tendonitis or Adult Acquired Flatfoot is another term used to depict the Painful progressive flatfoot. This occurs when the posterior tibial tendon gets inflamed or injured. The posterior tibial tendon helps to concord the arch in proper position and when this tendon in damaged, a painful lowering or collapse of the curvation develops. Chronic rigid flat human foot and functional limb length discrepancies can occur if left untreated. Severely rigid apartment anxiety can also atomic number 82 to posterior tibial tendonitis due to the constant strain of the tendon.
Prolonged periods of time allows our pes to collapse affecting our gait and posture, which can lead to a tremendous amount of stress not only to the pes simply to the remainder of the body. Our feet naturally pronate during the gait cycle, however when we have apartment feet we pronate for a longer flow of fourth dimension which and then alters the biomechanics and distribution of pressure and weight across the foot. This imbalance may increment the progression of underlying foot deformities such as bunions and hammertoes and lead to painful atmospheric condition associated with excessive pronation such as arch/ heel pain, shin splints/ posterior tibial tendonitis, and achilles tendonitis. This imbalance can and then translate upward affecting other parts of the body such as our knees and back.
Normal arch: The normal arch allows weight and pressure to be evenly distributed across the pes to minimize faulty biomechanics that may affect not just the feet, but also the ankles, knees, and dorsum.
High arch: High arches don't necessarily cause hurting, though your foot can feel more than fatigued and sore when yous have them. People with high arches have an increased amount of weight placed on the ball and heel of the human foot when walking or standing. This can result in pain and difficulty with posture and balance. People with high arches too accept a greater tendency to suffer from ankle sprains as anxiety supinate and gyre inward. Having a high arch can too lead to lateral (outside) genu hurting equally the inward rolling of the feet crusade the knees to turn outward.
DOES EACH Bear on YOU WHEN YOU Piece of work OUT?
Apartment feet: Working out just exacerbates what was mentioned above in terms of the negative touch excessive pronation has on the foot. The damage happens faster and harder.
High curvation: Having high arches means that less of your foot actually touches the ground when walking or running, providing less shock absorption when the foot strikes the ground. Therefore, people with loftier arches can be more decumbent to overuse injuries when playing sports or exercising. Highly biconvex anxiety can likewise make it difficult to fit into regular shoes. Trying to wearable shoes without enough room or support to conform a high arch can exist painful because more stress is placed on the metatarsals ultimately leading to hurting in the ball of the anxiety known every bit metatarsalgia equally well as plantar fasciitis.
WHAT TYPE OF SHOES/Back up SHOULD EACH TYPE LOOK FOR?
Flat anxiety: Those with flat feet should look for the following support:
- Spacious toe box that allows your toes to motility freely with no restrictions therefore minimizing discomfort placed on flat arches.
- Well-cushioned footbed and anatomical arch support to hold the plantar fascia and prevent it from collapsing to minimize fatigue and pain associated with flat feet.
- Deep heel cup to maintain proper human foot realignment and maintain pressure level relief of the plantar fascia with heel strike. This will aid maintain proper sagittal motion and minimize frontal plane motion which tin lead to excessive pronation, collapse of the arch, and ultimately foot hurting associated with flat feet.
Loftier arch: Those with high arches should await for the following support:
- Shoes with specifically engineered foot beds and molded EVA midsoles such equally Brooks Beast, Mizunos, Asics, and are designed to assistance mitigate foot, heel, and arch support for superior comfort and support of the plantar fascia.
- Rigid shank: In order to tell if the shoe is rigid enough, you want to accept the shoe and bend information technology in half. You shouldn't be able to, because the shank is the actual structure of the shoe and should be rigid to concord up and support the arch.
- Rigid heel counter: Squeeze the heel of the shoe to see how firm it is. There should be a expert bit of padding called an ankle collar which is intended to protect and absorber the ankle and the achilles tendon. You shouldn't be able to compress it - so when y'all are running it supports the heel which will help prevent ankle sprains in people with high arches. The heels of the shoe should be a little wider on the bottom to add stability.
WHAT ELSE IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW Near YOUR Foot ARCH?
Your arch can collapse over time due to activities, weight gain, and ligamentous laxity as the foot loses collagen with age and after pregnancy.
hendricksoncarapt.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.gothamfootcare.com/blog/know-your-arch-type/

0 Response to "How to Know if You Have High Arch Feet"
Post a Comment